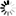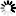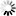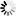Operator Library: Base
Library: Base
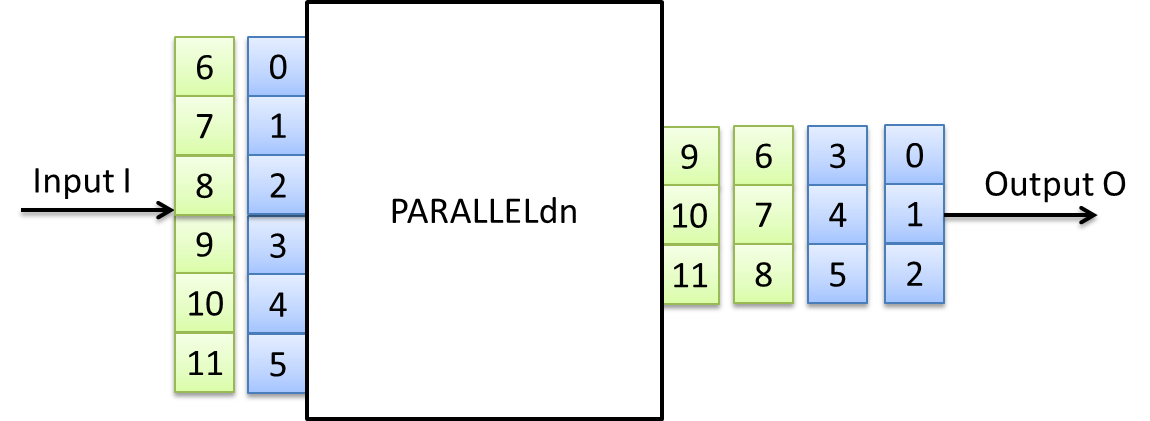
The operator PARALLELdn decreases the parallelism between the input link and the output link.
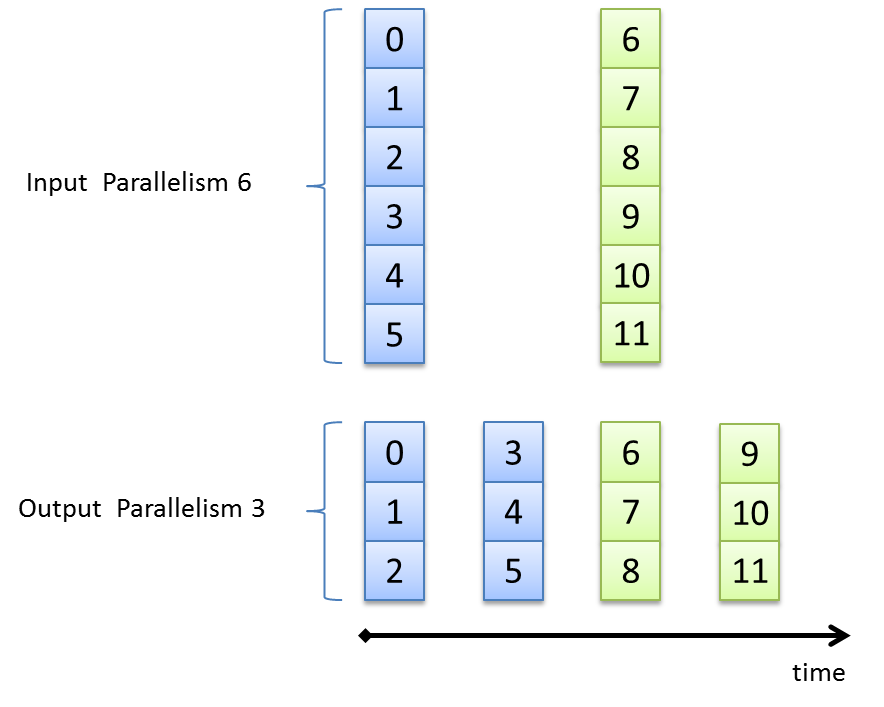
Following figure shows a parallel down conversion from parallelism 6 at the input down to parallelism 3 at the output.
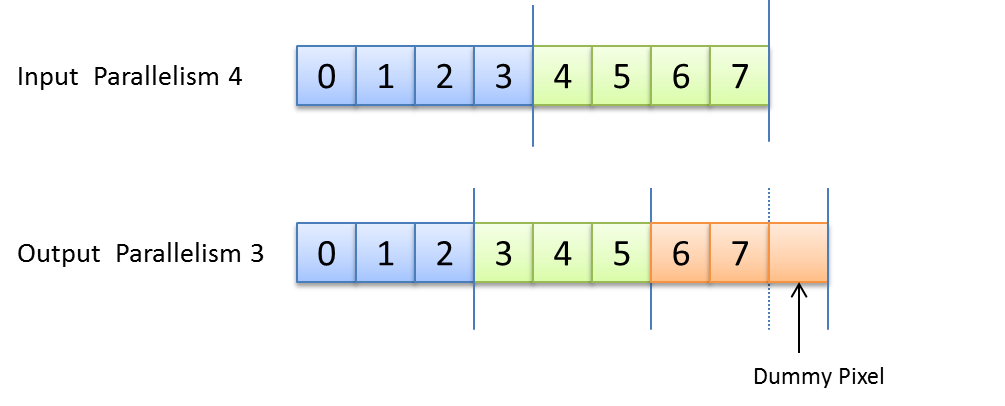
In VisualApplets, the width of an image line has to be a multiple of the parallelism. As the PARALLELdn operator allows any parallelism at its output it is possible that the width of a image line at the output is not a multiple of the output parallelism. In this case the operator will add dummy pixels to fill up the image line. The value of this dummy pixel is undefined. In VA simulation dummy pixels will be set to zero for better visibility.
The following figure shows in illustration of this dummy pixel insertion. As can be seen, the output parallelism of three cannot map the input line width of eight. Here, one extra dummy pixel is added so that the line width becomes nine.
Note that a parallelism decrease will result in a lower bandwidth of the output link compared to the input link. As the operator cannot buffer data, the reduced output bandwidth is also present at the input and might influence the precedent operators in the image pipeline. Technically, the input of the operator is closed/blocked for some clock cycles at a parallel down conversion. The following figure illustrates the timing of the operator.
The operator requires fewest resources if the input parallelism is an integer multiple of the output parallelism.
|
The range of the input bit width is [1, 64] for unsigned values. For signed inputs, the range is [2, 64]. For unsigned color inputs [3, 63] and for signed color inputs [6, 63]. |
|
|
The output image width must not exceed 2^31-1. The maximum image width at the output is automatically rounded to the next multiple of O.Parallelism. As a result, I.MaxImgWidth must not be greater than 2^31-1-O.Parallelism so that the rounded maximum image width at the output doesn't exceed 2^31-1. |
The use of operator PARALLELdn is shown in the following examples:
-
Bandwidth Bottlenecks - Reducing the parallelism after the removal of pixels.
-
Examples - Shows the usage of operator Blob_Analysis_1D in line scan applications.
-
'Color Plane Separation Option 5 - Sequential Output with Advances Processing'
Example on separation of color planes. The RGB input is split into its component and sequentially output via one DMA channel. The splitting if performed by collecting same components in parallel words and reading with FrameBufferRandomRead.
-
Examples - A high speed and robust laser line detection algorithm. The algorithm determines center of gravity coordinates to obtain sub-pixel resolution results.
-
Examples - Demonstration of how to use the operator


 Prev
Prev