Operator Library: Arithmetics
Operator SUB calculates the difference between input link I1 and input link I2 i.e. O = I1 - I2
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Operator Type | O |
| Input Links | I1, data input I2, data input |
| Output Link | O, data output |
| ImplementationType | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | static write parameter | |||
| Default | AUTO | |||
| Range | (AUTO, EmbeddedALU, LUT) | |||
|
Parameter ImplementationType influences the implementation strategy of the operator, i.e., which logic elements are used for implementing the operator. You can select one of the following values: AUTO: When the operator is instantiated, the optimal implementation strategy is selected automatically based on the parametrization of the connected links. EmbeddedALU: The operator uses embedded arithmetic logic elements of the FPGA that are not LUT based. LUT: The operator uses the LUT logic of the FPGA.
|
||||
The use of operator SUB is shown in the following examples:
-
Example - Histogram thresholding
-
Examples - The blob analysis operator is applied to an input camera image. The applet shows the usage of the blob data in the applet. In this case, the object with the maximum are is localized and the coordinates are used to cut out the object from the original image.
-
Examples - Calculates the differences between two successive images. The differences are thresholded and output via DMA channel.
-
Example - Calculates image moments orientation and eccentricity
-
Examples - Shows how to vertically mirror an image. Note the mirroring of the parallel words and the pixel.
-
Examples - The examples shows an automatic dead pixel detection and replacement.
-
Examples - The example shows the implementation of a 2D shading correction. Correction values are stored in frame grabber RAM. The applet performs a high precision offset and gain correction.
-
'2D Shading Correction / Flat Field Correction Using Operator RamLUT'
Examples - The example shows the implementation of a 2D shading correction. Correction values are stored in the operator RamLUT. The applet performs a high precision offset and gain correction.
-
'1D Shading Correction Using Block RAM'
Examples - The example shows an 1D shading correction. The correction values are stored in block RAM memory.
-
'1D Shading Correction Using Frame Grabber RAM'
Examples - The example shows an 1D shading correction. The correction values are stored in Frame Grabber RAM.

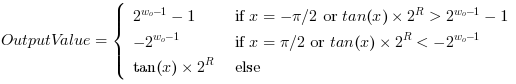
![[Note]](../common/images/admon/note.png)
 Prev
Prev