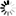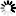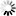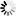Operator Library: Arithmetics
The operator calculates the arctan of the input.
The input range of arctan is [∞, ∞]. This operator includes a parameter Resolution to define the fixed point resolution bits of the input values. The input range is given by the number of input bits =
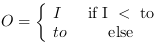
where
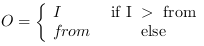
is the bit width at the input and R the resolution bits.
The argument x of the arctan function is determined by
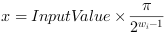
The results of the arctan function are in the range ]- π/2, π/2[. The output value range of the operator in VisualApplets is mapped to
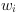
where
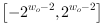
is the bit width at the output link. Thus the output value is
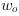
The following image shows the plot of the arctan function.
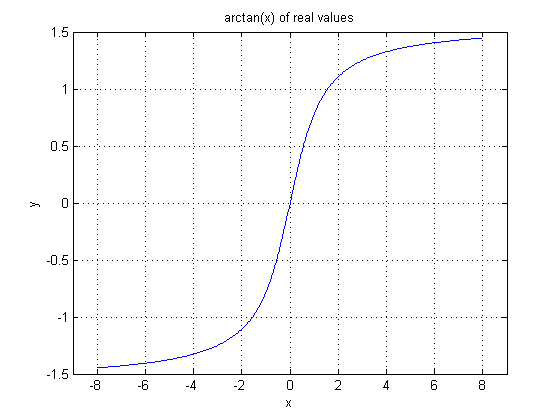
In the next figure, the VisualApplets operator implementation is shown. Note the input and output bit widths.
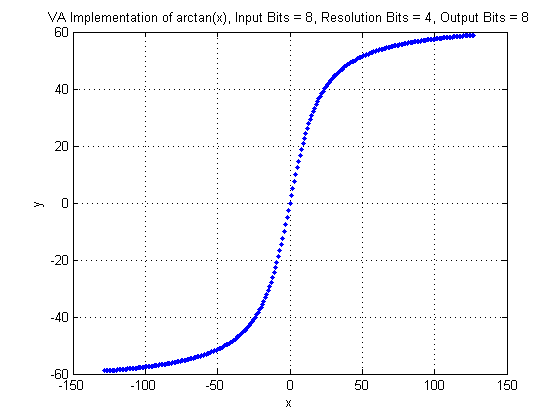
Le't have a look at an input pixel value. For example -50. With the given resolution of four, the real value representation of the pixel value is -50/16. The arctan result of -50/16 is arctan(-50/16) = -1.26. In pixel value representation this result becomes -51,38 which is the same as shown in the plot.
| Link Parameter | Input Link I | Output Link O |
|---|---|---|
| Bit Width | [8, 12] | [8,32] |
| Arithmetic | signed | signed |
| Parallelism | any | as I |
| Kernel Columns | 1 | as I |
| Kernel Rows | 1 | as I |
| Img Protocol | {VALT_IMAGE2D, VALT_LINE1D, VALT_PIXEL0D} | as I |
| Color Format | VAF_GRAY | as I |
| Color Flavor | FL_NONE | as I |
| Max. Img Width | any | as I |
| Max. Img Height | any | as I |
| ResolutionBits | |
|---|---|
| Type | static parameter |
| Default | 8 |
| Range | [0, OutputBitWidth] |
|
This parameter defines the accuracy of the input values as defined in the description above. |
|
The use of operator ARCTAN is shown in the following examples:
-
Example - Calculates image moments orientation and eccentricity
-
'Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG)'
Examples- Histogram of oriented Gradients
-
'Functional Example for Specific Operators of Library Arithmentics: Trigonometric Functions'
Examples - Demonstration of how to use the operator

 Prev
Prev