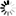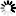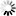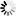Operator Library: Base
The operator merges N input links to a single output link by concatenating the input links to parallelism components. The following images illustrate 2 cases: In case A, 3 input links of parallelism 1 are merged. In case B, 3 input links of parallelism 2 are merged.
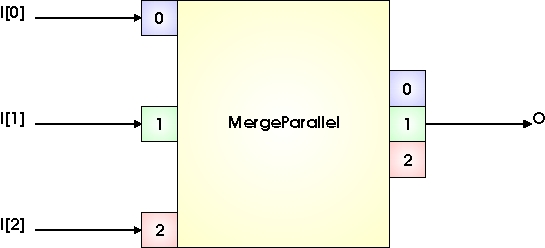
The input parallel pixels are concatenated to a single output link of parallelism 3. The input link order determines the position of the corresponding pixel in the parallel output.
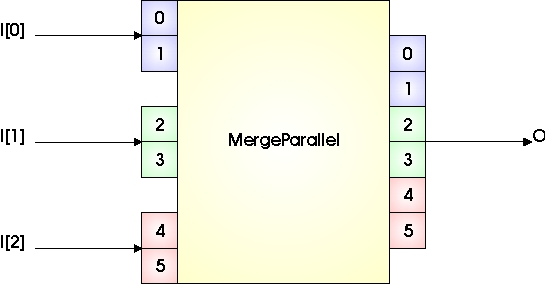
Note that input pixels in this case are also concatenated to the parallel output and are not interleaved. The 3 input links of parallelism 2 are concatenated to the output link of parallelism 6.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Operator Type | O |
| Input Links | I0, data input I[n], n > 0, data input |
| Output Link | O, data output |
|
The range of the input bit width is [1, 64]. For signed inputs, the range is [2, 64]. For unsigned color inputs, the range is [3, 63] and for signed color, the range is [6, 63]. |
|
|
The output parallelism is the sum of the input parallelism of all input links. |
|
|
The output maximum image width is the sum of the input maximum image widths of all input links. |
| MergeMode | |
|---|---|
| Type | static parameter |
| Default | Append |
| Range | {Append, Interleave} |
|
This parameter defines the way how pixel from the input links are arranged in the output link.
Append: All parallel pixel of each input link are appended.
Example: If you have 3 input links of parallelism 2 then you get an output link of parallelism 6. The first 2 pixel are taken from I0, then 2 pixels from I1, and finally 2 pixels from I2.
Interleave: Pixels are interleaved round robin over the input links.
Example: If you have 3 input links of parallelism 2 then you get an output link of parallelism 6. The parallel pixels in the output link get arranged as follows: pixel 0 of I0, pixel 0 of I1, pixel 0 of I2, pixel 1 of I0, pixel 1 of I1, and finally pixel 1 of I2.
|
|
The use of operator MergeParallel is shown in the following examples:
-
Example - Histogram thresholding
-
Examples - Shows the usage of operator Blob_Analysis_1D in line scan applications.
-
Examples - Shows the usage of operator Blob_Analysis_2D. The applet binarizes the input data and determines the blob analysis results. The results as well as the original image are output using two DMA channels.
-
'Color Plane Separation Option 5 - Sequential Output with Advances Processing'
Example on separation of color planes. The RGB input is split into its component and sequentially output via one DMA channel. The splitting if performed by collecting same components in parallel words and reading with FrameBufferRandomRead.
-
Example - For debugging purposes the Scope operator provides options for analyzing gray-scale pictures. .
-
Examples - Downsampling by factor 3x3 without the use of operator SampleDn.
-
Examples - Shows how to vertically mirror an image. Note the mirroring of the parallel words and the pixel.


 Prev
Prev