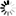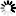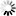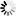Operator Library: Arithmetics
The operator calculates the sine of the input.
The input range of the sine function is [-∞, ∞]. Because of the periodicity of the sine function the input range of the VisualApplets operator is limited to [-π, π] i.e. the minimum value at the input is -π and the maximum value at the input plus 1 is π. Thus, it it not possible to have the value +π at the input.
The argument x of the sine function is therefore determined by
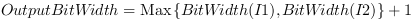
where
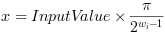
is the bit width at the input link.
The results of the sine function are in the range [-1, 1]. The output value range of the operator in VisualApplets is mapped to
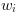
where
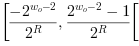
is the bit width at the output link. Thus the output value is
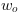
The following image shows the plot of the sine function.
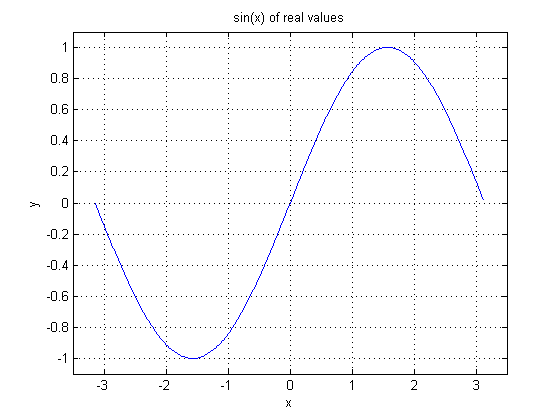
In the next figure, the VisualApplets operator implementation is shown. Note the input and output bit widths.
Le't have a look at an input pixel value. For example -50. With the given input bit width of 8, the real value representation of the pixel value is -50 * pi / 128. The sine result will then be -0.94. In pixel value representation this result becomes -121 which is the same as shown in the plot.
| Link Parameter | Input Link I | Output Link O |
|---|---|---|
| Bit Width | [8, 12] | [8, 32] |
| Arithmetic | signed | signed |
| Parallelism | any | as I |
| Kernel Columns | 1 | as I |
| Kernel Rows | 1 | as I |
| Img Protocol | {VALT_IMAGE2D, VALT_LINE1D, VALT_PIXEL0D} | as I |
| Color Format | VAF_GRAY | as I |
| Color Flavor | FL_NONE | as I |
| Max. Img Width | any | as I |
| Max. Img Height | any | as I |
The use of operator SIN is shown in the following examples:
-
Example - For debugging purposes the Scope operator provides options for analyzing gray-scale pictures. .
-
'Geometric Transformation and Distortion Correction'
Examples- Geometric Transformation and Distortion Correction using PixelReplicator
-
'Functional Example for Specific Operators of Library Arithmentics: Trigonometric Functions'
Examples - Demonstration of how to use the operator

 Prev
Prev